Introduction:
One of the core cultural values I found quite hard to grasp in New Zealand is the inherent egalitarian nature of Kiwis. It shows that Kiwis are friendly, respectful, and courteous of others. Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern’s viral catchphrase “Be Kind” symbolically embodies our culture. However, are there potential negative consequences because of our egalitarianism? I wondered whether if it was why we have a ‘tall poppy syndrome’ problem.
As Dr Oliver Hartwich mentioned in his recent column for The New Zealand Herald, New Zealanders have a lax attitude towards excellence. Although, we have a few world-class sportspeople, business CEOs and others. But as a society, it seems as though we put more emphasis on equality rather than excelling in anything. I’ve personally witnessed this through the Kiwi nature of the ‘Yeah, nah, yeah bro’ attitudes towards life. ‘She’ll be alright mate’ is the common answer we raise whenever we face internal troubles or domestic difficulties. This has had unintended consequences across the country reflected in our economic and social outcomes. I think New Zealand has a broad cultural problem – if most Kiwis take a complacent attitude towards life, we will witness a further decline. This starkly contrasts countries that outperform us such as East Asian nations like South Korea and Singapore.
Economic and Social Indicators:
Our ‘average’ international rankings speak for itself. Our international education standards have fallen substantially in the last few decades. In PISA, our scores dropped for Maths, Science and Reading substantially shown in Briar Lipson’s book ‘New Zealand’s Education Delusion’. Our productivity gap between Australia has continuously widened closer to 20%. Our economy is still heavily reliant on primary industries and international tourism, despite being a developed economy. Our FDI restrictiveness is number one in the OECD. Our Universities are nowhere near the top 50 in the world (In contrast to our neighbours Australia, which have more than 5 Universities). There are other economic and social indicators that I could mention, but the reality is that if Kiwis continue to be satisfied with mediocre economic, social and government policies, then our whole society will ‘pay’ for such mediocrity in the long term.
The Dramatic Turnaround of East Asia: From Developing to World-Class
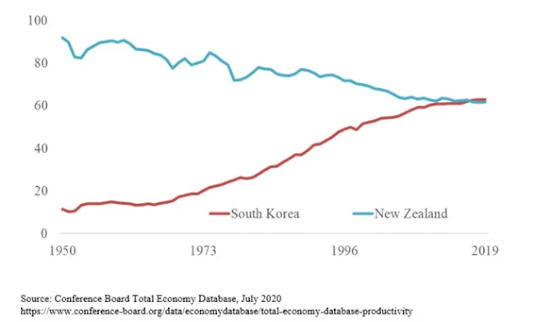
Figure 1: Labour Productivity Levels Relative to the United States (%), 1950-2019 (S. Korea & NZ)
Internationally, countries in Asia (especially North-East Asia) witnessed a remarkable economic recovery beginning during the post-WWII period. Beginning with Japan’s industrialisation, the new four Asian Tigers – South Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong and Singapore followed suit with the ‘flying geese’ model of economic development. Economists have coined these four countries’ world-class economic outcomes as the ‘East Asian miracle’. Coincidently, this contrasts starkly with New Zealand’s mediocrity witnessed in the last 70 years.
Economist Dr Üngör of Otago raised this in his recent Newsroom column. As shown in Figure 1, South Korea’s labour productivity level was less than 12% of US labour productivity in 1950, but by 2019 it was 63%. New Zealand was at 92% of the US in 1950 but dropped to 62% by 2019. The figure provides a humbling picture for New Zealand – The South Koreans have overtaken New Zealanders and we are falling behind the best performers in the world today. Back then, New Zealand was once one of the few nations with one of the highest GDP per capita in the world, but since then we have faltered into a mid-tier economy.
South Korea’s overlap of New Zealand should signal warning signs for New Zealand policymakers. The turnaround was possible because South Koreans built a prosperous nation by changing the cultural narrative towards competency, strived for excellence, and took greater communitarian responsibility towards long term prosperity. A similar change of mantra can be said about the Taiwanese and the Hong Kong people.
My personal favourite example is the South East Asian city-state Singapore. With the brilliant leadership of Lee Kuan Yew, the nation went from a wasteland with no natural resources into one of the finest economics in the world. His style of government was highly technocratic. Singapore is very competitive, meritocratic, and pursues economic policies that were practical and results-driven. A combination of state-intervention and liberal free markets, it’s the fourth-highest in the world for GDP per capita. Not only is the country extremely efficient, but it is also environmentally friendly and clean. A perfect combination of sustainable development and world-class governance. Whilst the nation is regarded as a semi-democratic society, there are many things New Zealand can learn from Singapore’s system, institutional mechanisms and broad culture. Lee changed the mindset of the Singaporean people to strive to excellence and competence.
Competent Response to Covid-19: South Korea and Singapore
In the earlier months of 2020, when Covid-19 hit the globe, the most effective responses were from East Asian states. I researched Taiwan, Singapore and South Korea during that period. They all had an exceptional public administration, competent execution of contact tracing, regular mask-wearing, mass testing of people and a well-mandated epidemic response team in their governments. These countries did well because they had a well-functioning society with the high-level expectation of competence and excellence. With these cultural factors in mind, they have world-class healthcare, government bureaucracies, a knowledge-based education curriculum and of course a competent response to Covid-19. This would have been impossible without having excellent administrators and a well-educated population.
New Zealand’s Covid-19 Response: Mixed Bag
New Zealand did very well responding to Covid-19 as well. However, I give much of the credit to our geographic proximity from the world. We were far away from epidemic centres such as China and Europe during the early stages of the pandemic. In addition, having Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern – not some of her Cabinet members – at the time was essential to keeping the public disciplined in our efforts to contain the virus. The lockdown was effective at stamping out the virus, but with an economic cost. Our Debt/GDP ratio is now projected to be 56% by 2026, despite beginning at 19.2% earlier before the national shutdown occurred.
Although this global pandemic is unprecedented, if we had the ambition and the drive to stamp out the virus without a national lockdown, I truly believe that would have been entirely possible. Our border quarantine procedures are still mediocre at best – after more than 9 months of Covid-19 – and blunders have caused the continuous resurrection of the virus in Auckland for the second time after complete elimination. It seems New Zealanders are ‘happy’ with the outcome without realising the combination of luck, public discipline, geographic proximity, and sound leadership. We have witnessed numerous examples of bureaucratic incompetence and administrative blunders in contrast to the East Asian states I mentioned before. Our contact tracing, testing, and border quarantine are still woeful in comparison.
Confucianism: The Cause of East Asian prosperity?
Perhaps some people might consider this East Asian trait of “excellence, merit and competence” as a broad Confucian phenomenon. Although Confucius himself did say:
“The will to win, the desire to succeed, the urge to reach your full potential… these are the keys that will unlock the door to personal excellence.”
But I can’t entirely agree with the view that it’s just a Confucian phenomenon. Cultural change across societies depend on the decisions policymakers or what individuals themselves make. For instance, Japan industrialised as a result of forced trade embargoes imposed by the Americans under Commodore Perry which led to the prosperous Meiji period. Historical critical junctures and circumstances are what changes societal culture.
The same thing can be said about the state of the Western world. Our cultural values have moved away from excellence towards equity. Previously, the West was leading the world on every economic, social and civilisational metric as indicated by historian Niall Ferguson. But now, the West – including New Zealand – are not as reputable as the past and the rise of Asia proves this declining trend. The West has lost the vital cultural component to its prosperity – The Weberian characteristics of work ethic, hard work and most importantly the strive for excellence.
Conclusion: Cultural Rejuvenation is an Imperative
New Zealand needs to renew this virtue of competence, excellence and merit. Whilst egalitarian values are important to keep society strongly harmonious with good social cohesion and trust, it is imperative that we recover our prioritisation towards excellence once again. We see this with our excessive cultural obsession with diversity and inclusion. Tolerance and social justice values are indeed important, but without a prosperous and thriving domestic economy, these values mean nothing. We must rejuvenate our old virtues of excellence in New Zealand. Across our education standards and our economic performance in the last few decades, we have so far settled with mediocrity.
The comparison and contrast between East Asian nations and New Zealand show us a few things. New Zealand is not good enough, we have been mediocre and sub-par at best across multiple performance indicators. We need to be more ambitious as a society for the long-run and we must rebuild our cultural values towards discipline, hard work, excellence and competence.